
What is EDI?
EDI, which stands for electronic data interchange, is the intercompany communication of business documents in a standard format. The simple definition of EDI is a standard electronic format that replaces paper-based documents such as purchase orders or invoices. By automating paper-based transactions, organizations can save time and eliminate costly errors caused by manual processing. In EDI transactions, information moves directly from a computer application in one organization to a computer application in another. EDI standards define the location and order of information in a document format.
Electronic data interchange (EDI) enables business users homogenize diverse structures of identical datasets (such as orders, delivery notes, invoices, inventories, price catalogs, etc.,) to speed up digital transactions with minimum error, at maximum speed, with the lowest cost.
What are EDI integrations?
EDI integrations refer to the process of connecting and integrating Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) systems with other internal or external systems to enable seamless data exchange and automate business transactions.
EDI integrations involve establishing connections between different systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, supply chain management (SCM) systems, and trading partner systems. The goal is to enable the electronic exchange of business documents in a standardized format, such as purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and more.
Here are some key aspects of EDI integrations:
- Data Translation: EDI integrations involve converting data from internal or external systems into the standardized EDI format and vice versa. This includes mapping data elements, fields, and segments between different systems to ensure seamless data exchange.
- Communication Protocols: EDI integrations use specific communication protocols, such as AS2 (Applicability Statement 2), FTP (File Transfer Protocol), or VAN (Value Added Network), to facilitate secure and reliable data transmission between systems.
- Trading Partner Onboarding: EDI integrations require establishing connections and setting up trading partner profiles to exchange data with external entities, such as suppliers, customers, or logistics providers. This involves configuring EDI communication parameters, document formats, and validation rules specific to each trading partner.
- Error Handling and Acknowledgments: EDI integrations include mechanisms to handle errors and validate the received data. This involves generating acknowledgments (e.g., EDI 997 Functional Acknowledgment) to confirm successful data transmission or resolving any issues encountered during the integration process.
- Automation and Workflow: EDI integrations often involve automating business processes and workflows based on the received EDI data. For example, automatically creating sales orders in the ERP system upon receiving a purchase order via EDI or updating inventory levels based on shipping notices.
Benefits of EDI Integrations:
- Streamlined Operations: EDI integrations eliminate manual data entry and paper-based processes, reducing errors, processing time, and administrative costs.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automated data exchange and streamlined workflows enable faster order processing, improved inventory management, and shorter lead times.
- Improved Accuracy: EDI integrations ensure data consistency and accuracy by eliminating manual data re-entry and reducing the risk of human errors.
- Stronger Trading Partner Relationships: EDI integrations promote smoother collaboration with trading partners by facilitating seamless data exchange and reducing communication barriers.
In conclusion, EDI integrations play a crucial role in enabling electronic data exchange and automating business transactions. They streamline operations, enhance efficiency, improve accuracy, and foster stronger relationships with trading partners, ultimately contributing to increased productivity and business success.
What is SAP IDoc?
IDoc is an SAP object that carries data of a business transaction from one system to another in the form of electronic message. IDoc is an acronym for Intermediate Document. The purpose of an IDoc is to transfer data or information from SAP to other systems and vice versa. The transfer from SAP to non-SAP system is done via EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) subsystems whereas for transfer between two SAP systems, ALE is used.
In order to enable the transfer of transactional information and ultimately reap benefits, business users will need an IDoc (Intermediate Document) which is an SAP file format. These IDocs further need to be integrated with EDI messages to streamline the transfer process. And here comes the role of an integration solution.
By mapping and integrating EDI messages with SAP IDoc formats, business users can streamline their B2B data exchange processes. The most common form of SAP EDI integration is performed using the SAP IDOC format, which is essentially a hierarchical flat file format developed by SAP to enable several types of data integration, including EDI.
SoftAt self-service-based solution makes it easy for all business users developers to integrate EDI messages with SAP IDoc and BAPI without excessively relying on IT or developer teams.
What Are the Advantages of SoftAt Solutions for EDI to SAP Integration?
- Easy to connect and send/receive IDoc or BAPI data, little coding needed
- Integrate SAP with any on-premise or cloud EDI application
- Rich SAP logs dashboard that shows the status of all the transactions
- Certified SAP Integration partner
- Outbound processing of a large amount of IDocs with multiple self-registering RFC servers.
- Inbound processing, i.e. transfer of IDocs to an R/3 system with an RFC client.
- Full implementation of tRFC in both RFC server and RFC client.
- Graphical mapping interface with data validation
- Meta-driven SOA framework to rapidly build and deploy new services into production
- Access to EDI data dictionaries, SAP IDoc and BAPI schemas
How Can Businesses Integrate EDI with SAP IDoc?
There are 2 simple steps to integrate an EDI message to SAP IDoc, in this example we will summarize the steps on how to map EDI 856 (Shipment Notice/Manifest) to SAP IDoc DELVRY03 document.
STEP 1: Map EDI to SAP IDoc
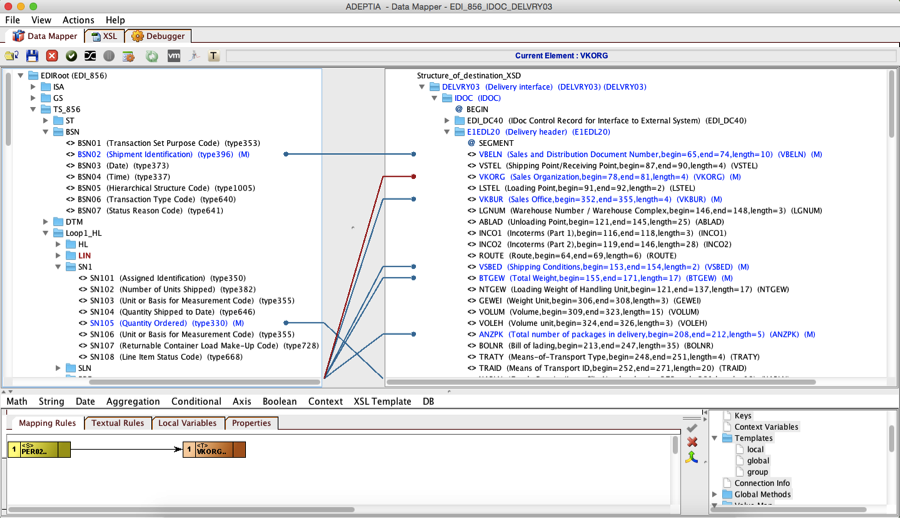
Create a mapping service between the inbound EDI to SAP IDoc. Adeptia’s AI-based graphical data mapper shows the specific EDI message schema and the IDoc schema. SoftAt SAP Adapter allows user to search for any IDoc automatically and select the particular IDoc that is needed for the SAP EDI mapping. The developer would then apply the mapping rules to convert the EDI to IDoc. This is a one-time effort since the mapping can be used in any orchestration where EDI 856 needs to be converted into SAP DELVRY03.
At run-time when the orchestration executes this data mapping service, the EDI data will be converted to IDoc.
Here’s an example of the EDI to IDoc mapping.
STEP 2: Deliver the IDoc to SAP through an orchestration
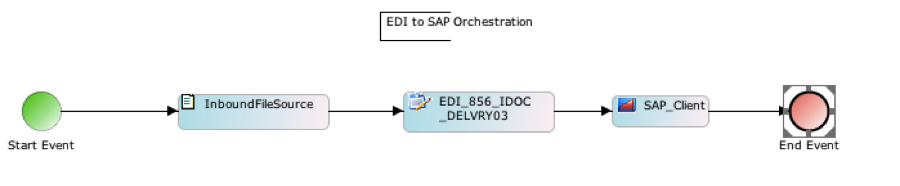
The final step is to design an orchestration that allows inbound EDI files to be delivered to SAP using the SoftAt SAP Adapter. Here’s a sample process of EDI idoc mapping in sap where an incoming EDI file is being sent to SAP PI/XI server. The mapping service created in step 1 is embedded as a second activity in the flow. Process picks up new EDI message and converts it to IDoc and delivers it to the SAP server.
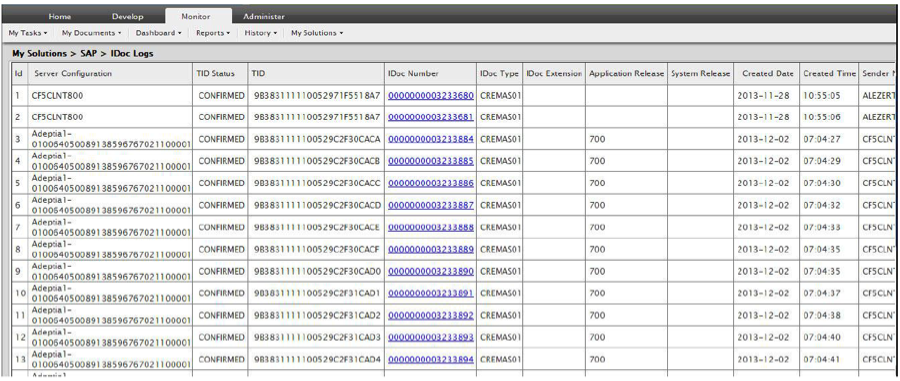
Run-time transactional logs are available to check the status of each transaction.
Is EDI the same as IDoc?
No, EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) and IDoc (Intermediate Document) are not the same, although they are related concepts within the SAP ecosystem.
EDI is a standard format used for the electronic exchange of business documents between different systems or trading partners. It enables the seamless transfer of structured data, such as purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and more, in a standardized and machine-readable format. EDI facilitates automated business transactions and promotes efficiency by eliminating manual data entry and reducing errors.
On the other hand, IDoc is a specific data format and technology used within the SAP system for exchanging data between different SAP applications or between SAP and non-SAP systems. IDocs are structured documents that contain business data in a specific format, allowing for consistent and reliable data exchange.
IDocs serve as the container for transferring data between systems, and they can represent various business transactions, such as sales orders, material master data, invoices, and more. IDocs are used for both inbound (data received by the SAP system) and outbound (data sent from the SAP system) communication.
While both EDI and IDoc facilitate electronic data exchange, IDoc is specific to the SAP ecosystem and is primarily used for communication between SAP applications or with external systems integrated with SAP. EDI, on the other hand, is a broader concept that encompasses various standards and protocols used for electronic data interchange across different systems and trading partners, including SAP systems.
In summary, EDI is a broader term that refers to the general concept of electronic data interchange, while IDoc is a specific format and technology used within the SAP system for exchanging data.
Services of SoftAt
SAP Consulting Services
- S/4 HANA Services
- SAP Template design & Implementation/Rollout
- SAP GST/GST Migration
- SAP Audit Services
- SAP Training
SAP Advanced Managed Services
- SAP ECC Services
- Rapid ERP Assessment Services.
- SAP Implementation Management Services.
- SAP Application Management Services.
- SAP Upgrade Management Services.
- SAP Application Training Services.
- Custom Application Development Services.
- ODATA / FIORI / UI5
- Enable Offline Functionality
- Custom Fiori client
- Enable RFID, Barcode scanning on Fiori
SAP Managed Services
- SAP Application Support Services
- SAP Offshore ABAP Development Services
- SAP Basis Support Services
- SAP Functional Support
- Application Interface management
SAP Development Services
- Application Development
- Development of a new application platform
- Enhancement / modification / migration of an existing application
- Interfaces to an existing application
- Correction of defects and deficiencies discovered by end-users
- Functionality Extensions
- Functional Help Desk
- Changes to the GUI to make it more user friendly





